Metabolisme Sel (Cellular Metabolism)
Metabolisme Sel (1)
Cellular Metabolism (1)
Cellular Metabolism (1)
Metabolisme berasal dari kata metabole yang berarti berubah. Secara istilah metabolisme bisa juga diartikan sebagai keseluruhan reaksi kimiawi suatu organisme (biologis). Metabolisme selalu terjadi pada setiap mahluk hidup, karena itu kematian dapat pula diartikan sebagai berhentinya metabolisme tubuh.
Metabolism derived from metabole which means change. Metabolism also can be interpreted as the overall chemical reaction of an organism (biological).Metabolism always occur in every living thing, that is why death can also be interpreted as a cessation of metabolism.
Metabolisme dapat digolongkan menjadi dua sebagai berikut :
Metabolims is divided into two, they are :
Metabolims is divided into two, they are :
- Katabolisme Catabolism
- Anabolisme Anabolism
Tapi sebelum membahas katabolisme dan anabolisme sebaiknya kita memahami dulu beberapa hal sebagai berikut.
But before discussing the catabolism and anabolisme we should first understand some of the following.
But before discussing the catabolism and anabolisme we should first understand some of the following.
A. Enzim Enzyme
Enzim merupakan biokatalisator yang berarti dapat memeprcepat reaksi biologi tanpa mengalami perubahan kimia. Enzim terdiri atas apoenzim yang mengandung protein dan gugus prostetik yang mengandung logam-logam. Gugus prostetik sendiri terbagi atas dua yakni kofaktor yang mengandung bahan anorganik dan koenzim yang mengandung bahan organik seperti vitamin B atau bagian vitamin. Cara kerja enzim dibagi ke dalam 2 jenis yakni :
Enzymes are biocatalyst which means it can support the biological reaction without undergoing chemical changes. The enzyme consists of apoenzim who containis protein and also prosthetic group who contains metals. Prosthetic group itself is divided into two they are cofactor who consist of anorganic material and coenzymes who contain organic materials such as vitamin B or part of vitamin. How enzymes work is divided into 2 way :
Enzymes are biocatalyst which means it can support the biological reaction without undergoing chemical changes. The enzyme consists of apoenzim who containis protein and also prosthetic group who contains metals. Prosthetic group itself is divided into two they are cofactor who consist of anorganic material and coenzymes who contain organic materials such as vitamin B or part of vitamin. How enzymes work is divided into 2 way :
1. Lock and key (Gembok dan Kunci)
Enzim dan substrat bekerja seperti kunci dan gembok. Enzim dimisalkan sebagai gembok, karena memiliki sisi kecil untuk bereaksi dengan substrat yang disebut sisi aktif.
Image source: lock key model
Enzyme and substrate work like Key and lock. The enzyme is assumed as a padlock, because it has a small side to react with the substrate, called the active side.
Enzyme and substrate work like Key and lock. The enzyme is assumed as a padlock, because it has a small side to react with the substrate, called the active side.
2.Induced Fit (Induksi Pas)
In this way enzyme can change it's form to suit the substrate.
Adapun beberapa faktor yang mempengaruhi kerja enzim sebagai berikut :
There are some factor who affect the work of enzyme :
There are some factor who affect the work of enzyme :
1. Temperatur atau Suhu (Temperature)
Enzim dapat bertahan pada suhu 0 derajat C, tapi rusak pada suhu >50 derajat C. Umumnya suhu optimum enzim adalah 30-40 derajat C.
Enzyme can stand in 0 degrees Celcius but damaged or destroyed at 50 degrees Celcius or more. Generally the optimum temperature of enzyme is about 30-40 degrees Celcius.
Enzyme can stand in 0 degrees Celcius but damaged or destroyed at 50 degrees Celcius or more. Generally the optimum temperature of enzyme is about 30-40 degrees Celcius.
2. pH
3. Konsentrasi enzim dan substrat (Concentration of Enzyme and Substrate)
Semakin tinggi konsentrasi enzim, reaksi akan berlangsung semakin cepat. Begitu pun sebaliknya, semakin tinggi konsentrasi substrat, maka kecepatan reaksi semakin berkurang.
The higher the concentration of enzyme, the reaction will run faster and faster.And vice versa, the higher the concentration of substrate, the speed of the reaction will decreased.
The higher the concentration of enzyme, the reaction will run faster and faster.And vice versa, the higher the concentration of substrate, the speed of the reaction will decreased.
4. Inhibitor (Inhibitor)
Inhibitor adalah penghambat kerja enzim. Ada dua jenis inhibitor yakni inhibitor kompetitif yang memiliki bentuk mirip dengan substrat sehingga masuk ke sisi aktif enzim dan menghalangi substrat serta inhibitor non kompetitif yang memiliki bentuk berbeda dengan substrat tetapi masuk ke sisi lain enzim sehingga sisi aktif enzim berubah dan substrat tidak dapat masuk. Beberapa contoh inhibitor adalah Kuprum, Seng dan Perak.
Inhibitor can disturb the work of enzyme. There are two types of inhibitor they arecompetitive inhibitor who has a similiar shape to the substrate then the inhibitor enter the active side of the enzyme and deters the substrate to get in to the enzyme and also non-competitive inhibitor whohas a different shape to the substrate but it enter another side of the enzyme (not the active side) so the active side changes it's form and the substrate cannot enter the enzyme and the eraction hampered. Some examples of inhibitors are Cuprum, Zinc and Silver.
Inhibitor can disturb the work of enzyme. There are two types of inhibitor they arecompetitive inhibitor who has a similiar shape to the substrate then the inhibitor enter the active side of the enzyme and deters the substrate to get in to the enzyme and also non-competitive inhibitor whohas a different shape to the substrate but it enter another side of the enzyme (not the active side) so the active side changes it's form and the substrate cannot enter the enzyme and the eraction hampered. Some examples of inhibitors are Cuprum, Zinc and Silver.
5. Aktivator (Activator)
Aktivator enzim dapat mempercepat kerja enzim seperti Magnesium dan Klor. Beberapa enzim harus diaktifkan oleh enzim lain sebelum dapat bekerja, seperti enzim Tripsinogen dalam sistem pencernaan kita yang dapat bekerja setelah diaktifkan oleh enzim Enterokinase.
Activator of Enzyme can support the work of the enzyme. Some examples are Magnesium or Clor. Some enzyme also need to be activated by another enzyme, for an example Tripsinogen is an inactive enzyme in our digestive system who can work after activated by Enterokinase enzyme.
Activator of Enzyme can support the work of the enzyme. Some examples are Magnesium or Clor. Some enzyme also need to be activated by another enzyme, for an example Tripsinogen is an inactive enzyme in our digestive system who can work after activated by Enterokinase enzyme.
Nah, sekarang baru kita masuk ke Katabolisme.
Now, lets discuss about Catabolism.
Now, lets discuss about Catabolism.
1. Katabolisme (Catabolism)
Katabolisme merupakan proses penguraian atau pembongkaran senyawa kompleks menjadi senyawa yang lebih sederhana. Proses ini disebut jugadesimilasi. Katabolisme bersifat eksoterm (menghasilkan energi). Salah satu contoh katabolisme adalah respirasi sel.
Catabolism is the process of decomposition or disassembly of complex compounds into simpler compounds. This process is also called desimilation.Catabolism is an exothermic reaction (produces energy). Example of catabolism is cellular respiration.
Catabolism is the process of decomposition or disassembly of complex compounds into simpler compounds. This process is also called desimilation.Catabolism is an exothermic reaction (produces energy). Example of catabolism is cellular respiration.
Respirasi sel terdiri atas beberapa tahap sebagai berikut :
Cellular respirationis consist of several stage :
Cellular respirationis consist of several stage :
1. Glikolisis (Glycolysis)
2. Dekarboksilasi Oksidatif (Oxidative Decarboxilation)
3. Siklus Krebs atau Siklus Asam Sitrat (Krebs Cycle or Citric Acid Cycle)
4. Transpor Elektron (Electron Transport Chain)
Yang akan dibahas adalah katabolisme Glukosa.
We will discuss about Glucose Catabolism.
We will discuss about Glucose Catabolism.
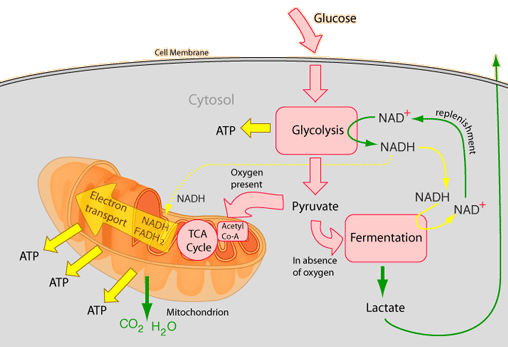
1. Glikolisis (Glycolysis)
Glikolisis terjadi di dalam sitoplasma sel dan merupakan rangkaian proses perubahan 1 molekul glukosa (6 karbon) menjadi 2 molekul asam piruvat (3 Karbon). Dalam glikolisis dihasilkan 4 ATP, 2 NADH dan menggunakan 2 ATP sehingga sering disebutkan menghasilkan 2 ATP dan 2 NADH. Glikolisis dapat berlangsung baik secara aerob maupun anaerob.
Glycolysis occurs in cytoplasm. It is a series of changement process of 1 glucose (6 Carbon) into 2 pyruvat acid (2 Carbon). Gycolysis produces 4 ATP and 2 NADH but also uses 2 ATP so we can conclude that Glycolysis produces 2 ATP and 2 NADH.
Glycolysis occurs in cytoplasm. It is a series of changement process of 1 glucose (6 Carbon) into 2 pyruvat acid (2 Carbon). Gycolysis produces 4 ATP and 2 NADH but also uses 2 ATP so we can conclude that Glycolysis produces 2 ATP and 2 NADH.
2. Dekarboksilasi Oksidatif atau Reaksi Antara atau Reaksi Transisi (Oxidative Decarboxilation or Transition Reaction)
Setelah glukosa dirubah melalui proses glikolisis menjadi asam piruvat, maka asam piruvat tersebut selanjutnya akan mengalami dekarboksilasi Oksidatif (DO) di dalam inermembran mitokondria. Asam privat yang memiliki 3 Karbon akan dirubah menjadi senyawa asetil yang memiliki 2 karbon. Karen itu salah satu karbon dilepaskan sehingga menghasilkan Karbondioksida, NADH dan kedudukannya digantikan oleh Koenzim A (KoA). Jadi hasil akhir dari DO adalah 2 NADH, 2 CO2 dan 2 Asetil KoA. Lho..kok dua sih? Ya dua. Soalnya 1 asam piruvat dari glikolisis menjadi 1 asetil KoA. Nah, kan hasil glikolisis itu 2 Asampiruvat, jadi dikali 2 deh.. :D
After the glucose changed into pyruvat acid, the pyruvat acid undergoes Oxidative Decarboxilation in intermembrane of Mitocondria. Pyruvat Acid who has 3 Carbon processed so ath the end of this stage the pyruvat acid changed into Acetil who has only 2 Carbon. 1 Carbon is released in form of Carbon dioxide and replaced by coenzymeA so the product of this stage is AcetilCoA. It also produce 2 Carbondioxide adn 2 NADH. Why 2 CO2 and 2NADH? The reason is because there are 2 Pyruvat acid who undergo this stage. remember, the glycolysis produces 2 pyruvat acid.
After the glucose changed into pyruvat acid, the pyruvat acid undergoes Oxidative Decarboxilation in intermembrane of Mitocondria. Pyruvat Acid who has 3 Carbon processed so ath the end of this stage the pyruvat acid changed into Acetil who has only 2 Carbon. 1 Carbon is released in form of Carbon dioxide and replaced by coenzymeA so the product of this stage is AcetilCoA. It also produce 2 Carbondioxide adn 2 NADH. Why 2 CO2 and 2NADH? The reason is because there are 2 Pyruvat acid who undergo this stage. remember, the glycolysis produces 2 pyruvat acid.
3. Siklus Krebs atau Siklus Asam Sitrat (Krebs Cycle or Citric Acid Cycle)
Siklus krebs terjadi di dalam matriks mitokondria dan secara total menghasilkan 4 CO2, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2 dan 2 ATP. Asetil KoA hasil dari reaksi transisi bergabung dengan oksaloasetat Karbon membentuk asam sitrat 6 Karbon yang kemudian mengalami siklus hingga kembali menjadi oksaloasetat.Ingat, 1 Siklus hanya menghasilkan 2 CO2, 3 NADH dan 1 ATP.
Kreb Cycle occurs in matrix of mitokondria and totally produces 4 CO2,6 NADH, 2 FADH2 and 2 ATP. AcetilCoA (product of Oxidative Decarboxilation, 2 Carbon) combined with Oxaloacetic (4 Carbon) and create Citric Acid (6 Carbon) who undergoes the cycle and be formed into Oxaloacetic again in the end of the process. Temember 1 Cycle ontly produce 3 NADH, 2 CO2 and 1 ATP.
Kreb Cycle occurs in matrix of mitokondria and totally produces 4 CO2,6 NADH, 2 FADH2 and 2 ATP. AcetilCoA (product of Oxidative Decarboxilation, 2 Carbon) combined with Oxaloacetic (4 Carbon) and create Citric Acid (6 Carbon) who undergoes the cycle and be formed into Oxaloacetic again in the end of the process. Temember 1 Cycle ontly produce 3 NADH, 2 CO2 and 1 ATP.
4. Transpor Elektron (Electron Transport Chain)
Selanjutkan energi-energi hasil dari ketiga tahap diatas memasuki tahap terakhir yakni transpor elektron. Dalam tahap ini energi (NADH,FADH2) dipak menjadi energi siap pakai (ATP). Transpor elektron terjadi pada membran dalam mitokondria. Elektron energi (H+) akan diterima oleh O2 (Oksigen) membentuk H2O(air).
Next stage, the energy of the previous stage enter the last stage, it is Electron transport Chain. In this stage the energy (NADH,FADH2) packaged into a ready to use energi namely ATP. This stage occur in the inner membrane of mitocondria. Electron (H+) will be accepted by O2 (Oxygen) to form H2O (water).
Next stage, the energy of the previous stage enter the last stage, it is Electron transport Chain. In this stage the energy (NADH,FADH2) packaged into a ready to use energi namely ATP. This stage occur in the inner membrane of mitocondria. Electron (H+) will be accepted by O2 (Oxygen) to form H2O (water).
Catatan : 1 NADH = 3 ATP, 1 FADH2 = 2 ATP dan 1 ATP ya 1 ATP aja..
Note : 1 NADH = 3 ATP, 1 FADH2 = 2 ATP
jadi berapakah total energi dari respirasi sel ini?
So, how much is the sum of energy in this cellular respiration?
So, how much is the sum of energy in this cellular respiration?
- Glikolisis (Glycolysis) : 2 NADH dan 2 ATP = 8 ATP
- Dekarboksilasi Oksidatif (Oxidative Decarboxilation) : 2 NADH = 6 ATP
- Sikus Krebs (Citric Acid Cycle) : 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, 2 ATP = 24 ATP
jadi total = 38 ATP.
So, the sum is 38 ATP.
So, the sum is 38 ATP.
Reaksi Pernapasan seluler dapat dituliskan :
The reaction of sellular respiration :
The reaction of sellular respiration :
C6H12O6--------->6CO2+6H2O+675kal+38ATP
(Respirasi aerob)
(Aerob Respiration)
(Aerob Respiration)
Lemak dan Protein tidak mengalami glikolisis melainkan langsung ke tahap Dekarboksilasi Oksidative.





Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar